Tendon Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis: What You Need to Know
Addressing tendon inflammation in individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is crucial due to its impact on pain, joint functionality, and overall quality of life. Tendonitis exacerbates existing discomfort, limits joint movement, and can lead to more severe complications if left untreated, such as tendon rupture and increased joint damage. Proper management not only prevents these issues but also enhances the effectiveness of RA treatments and empowers individuals to take an active role in their health. Ultimately, addressing tendon inflammation is vital for minimizing pain, preserving joint function, and improving the overall well-being of those with RA.
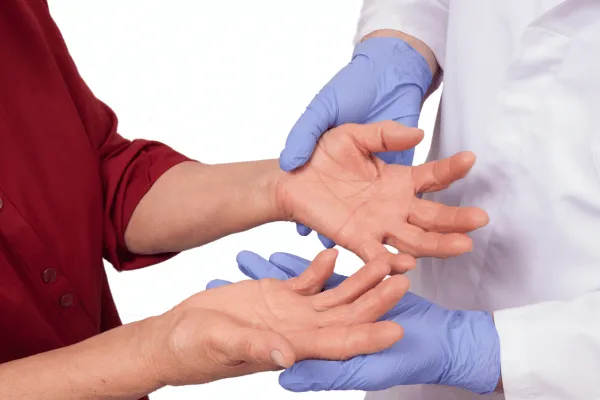
Tendon Inflammation (Tendonitis): Tendon inflammation, commonly referred to as tendonitis, is a condition characterized by the swelling and irritation of tendons – the tough, fibrous cords that connect muscles to bones. Tendons play a crucial role in facilitating joint movement by transmitting the force generated by muscles to the bones, enabling smooth and controlled motion.
Role of Tendons and Their Importance for Joint Movement: Tendons act as connectors between muscles and bones, serving as essential components of the musculoskeletal system. They transmit the force produced by muscle contractions to the bones, allowing joints to move in various directions. Without tendons, our muscles would be unable to exert their force on bones effectively, leading to impaired movement and diminished functionality.
Impact of Inflammation on Tendons and RA Symptoms: Inflammation can have a detrimental effect on tendons and exacerbate symptoms in individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). In RA, the immune system mistakenly targets healthy joint tissues, leading to chronic inflammation. When inflammation affects tendons, their structure can become compromised, leading to swelling, pain, and reduced flexibility.
As tendons become inflamed, their ability to transmit muscle force to the bones is hindered. This can result in joint stiffness, decreased range of motion, and discomfort during movement. Inflammation can also weaken tendons, making them more susceptible to injury and increasing the risk of conditions like tendon rupture.
The impact of inflammation on tendons can further compound the challenges faced by individuals with RA, intensifying the pain and mobility limitations already associated with the condition. By addressing tendon inflammation, it is possible to mitigate these effects, alleviate discomfort, and improve joint functionality for a better quality of life. Proper management of both RA and tendonitis is essential to minimize the negative impact of inflammation on tendons and overall joint health.
Tendonitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Connection:
The relationship between Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and tendonitis is underpinned by a commonality: inflammation. Both conditions are characterized by inflammation that affects joint tissues and tendons. In RA, systemic inflammation and autoimmune factors contribute to joint damage and pain, while in tendonitis, inflammation arises as a response to injury or strain. People with RA are more susceptible to developing tendonitis due to factors like synovial involvement, weakened tissues, altered joint mechanics, and overuse. Addressing both RA and tendon inflammation is vital to managing symptoms, preventing complications, and preserving overall joint health.
Emphasizing the utmost importance of early detection and personalized treatment for addressing tendon inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Swift intervention prevents complications, preserves joint function, and improves well-being. Effective RA management plays a crucial role in managing tendon inflammation, as it reduces systemic inflammation and indirectly safeguards tendons. Encouraging readers to actively seek guidance from healthcare providers, engage in open communication, and stay proactive in managing both RA and tendonitis. Collaborating with medical experts ensures informed decisions, better outcomes, and an enhanced quality of life.
Promoting Interventions That Reduce Arthritis Pain
American Arthritis Foundation recognizes several proven approaches to reduce arthritis symptoms:
Be active. Physical activity—such as walking, bicycling, and swimming—decreases arthritis pain and improves function, mood, and quality of life. Adults with arthritis should move more and sit less throughout the day. Getting at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity each week is recommended.
Protect your joints. People can help prevent osteoarthritis by avoiding activities that are more likely to cause joint injuries.
Talk with a doctor. Recommendations from health care providers can motivate people to be physically active and join a self-management education program. Should your arthritis be interfering with your activities of daily living you may be a candidate to receive many new treatments, and learn how to reverse the arthritis condition.
Have a question?
We're Here to Help
By providing my phone number, I agree to receive text messages from the business.



